Acute prostatitis is an infectious inflammation of the prostate gland, accompanied by swelling and the formation of purulent foci in the prostate. Symptoms of acute prostatitis depend on the stage (catarrhal, follicular, parenchymatous, abscessed) and it may contain dysuric disorders, pain in the perineum, fever, poisoning. Diagnosis is based on palpation of the prostate, ultrasound and Doppler-studium in the prostate, a study of discharge from the urethra and prostate secretion. Treatment of acute prostatitis includes the administration of antimicrobial therapy, Nsaids, antispasmodics, analgesics, immunomodulators, physiotherapy.
Acute and chronic prostatitis is the most common and socially significant diseases of man. Clinical urology, prostatitis is diagnosed in 30-58% of men in the reproductive and working age (30-50 years). Acute prostatitis is accompanied by disorders of sexual function and fertility, disorders of psychoemotional state and social disadaptation.
Causes of acute prostatitis
The causative agents of acute prostatitis are mainly non-specific pathogens, which penetrate into the tissues of the prostate, gram-negative (Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Proteus) or gram-positive (staphylococci, enterococci, streptococci)
Often acute prostatitis may be due to pathogens urogenital infections:
- chlamydia
- trichomoniasis,
- Ureaplasma,
- gonorrhea,
- mycoplasmosis,
- candidiasis etc.
In most cases the penetration of microbes, the prostate tissue occur transcanalicular way – through the excretory ducts of the glands in the wall of the posterior urethra. Therefore, the urethra of any origin is very often complicated with acute prostatitis. Less of the microbial flora into the prostate of the bladder acute cystitis. Pathogen glands is significantly facilitated by the increased intraurethral pressure (reprehenderit, stones in the urethra), the behavior of the endourethral manipulation (bougienage of the urethra, urinary catheterization, ureteroscopy, cystoscopy, etc.).
In addition, acute prostatitis can be the result of hematogenous infection, to facilitate the conditions on blood circulation in the prostate, which is a well-developed system of arterial and venous anastomoses. When called hematogenous drift of bacteria can get into the prostate tissue from distant foci of purulent tonsillitis, sinusitis, dental caries, cholecystitis, bronchitis, pyoderma, etc. Can lymphogenous infection of the prostate the rectum, anal fissures, proctitis, colitis.
Non-infectious factors affect the development of acute prostatitis are constant traffic jams in the veins of the pelvis and disruption of drainage and the spices of the prostate. Stagnation can be caused disritmia sexuality and sexual violations – is the practice of coitus interruptus, lack of or irregular sexual activity, excessive sexual activity, etc. The pathological deposition of blood in the venous line of the pelvis can be detected, while lack of exercise, frequent constipation, colds, chronic (mainly alcohol) poisoning, varicose veins of the pelvis.
Forms of acute prostatitis
The development of acute prostatitis distinguish the following forms, which are its steps:
- catarrhal,
- follicular
- parenchymal,
- abscessed.
Acute prostatitis begins with catarrhal inflammation of the mucous membrane and submucous layer of the excretory ducts of individual lobules of the gland. Further swelling of the walls of the channels to promote stagnation of Muco-purulent secret of the follicles of the prostate and progression of inflammation in the context of what may develop focal suppuration of lobules of acute follicular prostatitis. When multiple lesions of the lobules and a diffuse involvement of the parenchyma and interstitial tissue of the prostate of purulent inflammation, acute prostatitis will go to its next stage – parenchymal. If the case is the merger of small ulcers in the large hearth, forming an abscess of the prostate gland, which can be used to open the urethra, perineum, rectum or bladder.
Symptoms of acute prostatitis
Clinical symptoms of acute prostatitis similar stages. The most common symptoms are pain, disorders of urination and intoxication.
Acute catarrhal stage of prostatitis feel the weight and pain in the perineum. Dysuric disorders is characterized by painful, frequent urination, especially at night. The body temperature remains within normal limits, may be slightly elevated; intoxication is missing. Palpation examination of the prostate is not changed or slightly increased, little painful. Examination of the prostate secretion detects a rise in white blood cells of accumulation of Muco-purulent threads. Urine emptying of the excretory ducts and spices occur white blood cells. Prostate massage is usually impossible, because of the pain. Treatment begins with a catarrhal stage, acute prostatitis, lead to the recovery of 7-10 days.
Follicular form of acute prostatitis is manifested more brightly, accompanied by a dull aching of the perineum, irradiation of the penis, rectum or sacrum. Against this background, the urination painful and difficult, until the development of acute urinary retention. The act of defecation acute follicular prostatitis is also difficult because of the expressed pain. Because of the increase in body temperature to 38°C, reduced general condition. Palpation per rectum is determined is enlarged, dense, strong, asymmetrical prostate, sharply painful in some areas, when digital research. The urine is collected, when palpation of the thyroid gland, contains a large number of white blood cells and purulent strands, forming a turbid precipitate. Massage to get a prostate secretion in the follicular phase of acute prostatitis is contraindicated. With the powerful treatment of acute follicular prostatitis can favorably be resolved; otherwise, it moves on to the next, the parenchymal phase.
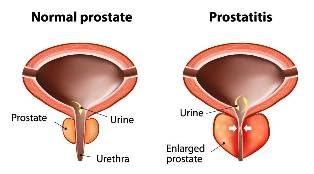
Clinic of acute parenchymatous prostatitis develops rapidly. Characterized by severe hyperthermia (39-39,5°C and above) with chills, General weakness, depression, loss of appetite, thirst. The first urination sharply learning and complicated, then you may stop altogether. Try to empty your bladder or bowel are accompanied by severe pain. Develop painful tenesmus, constipation, flatulence. The pain extends to the rectum, is pulsating in nature, forcing the patient to take a forced position – lying down with your legs crossed. With the development of reactive inflammation of the rectum, anus mucus.
Determined by palpation diffusely enlarged, with unclear outline of the gland, very painful at the slightest touch. Prostate massage parenchymal phase of acute prostatitis is contraindicated strongly. Sometimes, because of the pararectal tissue swelling and tenderness, rectal examination is not possible leads to. Urine – pronounced album sanguinem cellam, pyuria. Result acute parenchymatous prostatitis can run in the resolution of the disease, formation of an abscess in the prostate or chronic prostatitis.
Diagnosis of acute prostatitis
Recognition and identification of the stage of acute prostatitis is carried out by a urologist and based on a comprehensive physical examination, laboratory and instrumental research. Examination of the prostate through the rectum can be used to determine the size, consistency, unity, symmetry, cancer, pain reaction, foci of destruction, signs of purulent fusion of tissues. Palpation of the prostate acute prostatitis is performed very carefully, without rough pressure and massaging movements. Obtained the prostate secretion revealed an increase in the number of leukocytes and amyloid Taurus, reducing the number of lecithin granules.
Acute prostatitis, there is increased leukocyturia the third part of the urine and urine collected when the palpation of the prostate. By dividing the causative agent of acute prostatitis is necessary to perform bacterial, analysis of urine and urethral discharge with antibiotics, PCR examination of scrapings, blood cultures sanguinem cultura. The nature and severity dysuric disorders acute prostatitis is estimated using uroflowmetries.

Ultrasound of the prostate, with moderate pain syndrome can be performed transrectal; if severe pain reaction – transabdominal. Anoscopically estimated, the shape, the magnitude of the cancer, the presence of focal or diffuse changes, it sets the stage for acute prostatitis. The use of Doppler-studium allows for a detailed and differentiated to evaluate the vascularization of the prostate.
When planning surgical tactics in relation to the destructive forms of acute prostatitis are appropriate, CT or MRI of the pelvis.
Treatment of acute prostatitis
The leading role of acute prostatitis include the reason for treatment. You need the best possible appointment of antimicrobial (antibacterial, antiviral, antitrichomonal, antimycotic) drugs to suppress the reproduction of micro-organisms, glands and tissues of the urethra. Reduce cramps and painful urination prescribe analgesics, spasmolytics, and rectal candles Anaesthesinum or belladonna, heat microclysters. In the complex treatment of acute prostate inflammation used anti-inflammatory drugs, enzymes, immunomodulators, vitamins, infusion solutions.
Physiotherapy in the acute prostatitis is performed after decrease in acute symptoms. The objective is anti-inflammatory, decongestant, analgesic action, improves microcirculation and local immunity applied to the rectal electrophoresis, UHF-therapy, microwave therapy, prostate massage. Acute prostatitis shown to comply with bed rest, sparing diet, sexual peace.
When urinary retention on the background of acute prostatitis avoid to perform catheterization of the bladder, I prefer the troc-ette cystostomy. When abscess of the prostate occurs in the need for surgical intervention - opening and drainage of abscess cavity.
Cure acute prostatitis is to assess the structure of the tissue glands and its functions, normalizes the composition of the juice of the prostate, removal of pathogens, causes inflammation of body fluids.
Prediction and prevention
As a rule, in a timely manner and at a reasonable causal treatment leads to cupping of acute prostatitis. Abscess of the prostate or chronic inflammation occurs in advanced cases.
Prevention of acute prostatitis should include cleaning the infectious foci in the body, carrying and endourethral endovesical manipulations in accordance with the rules of asepsis, timely treatment of sexually transmitted diseases and the urethra, the normalization of sexual activity and physical activity.
























